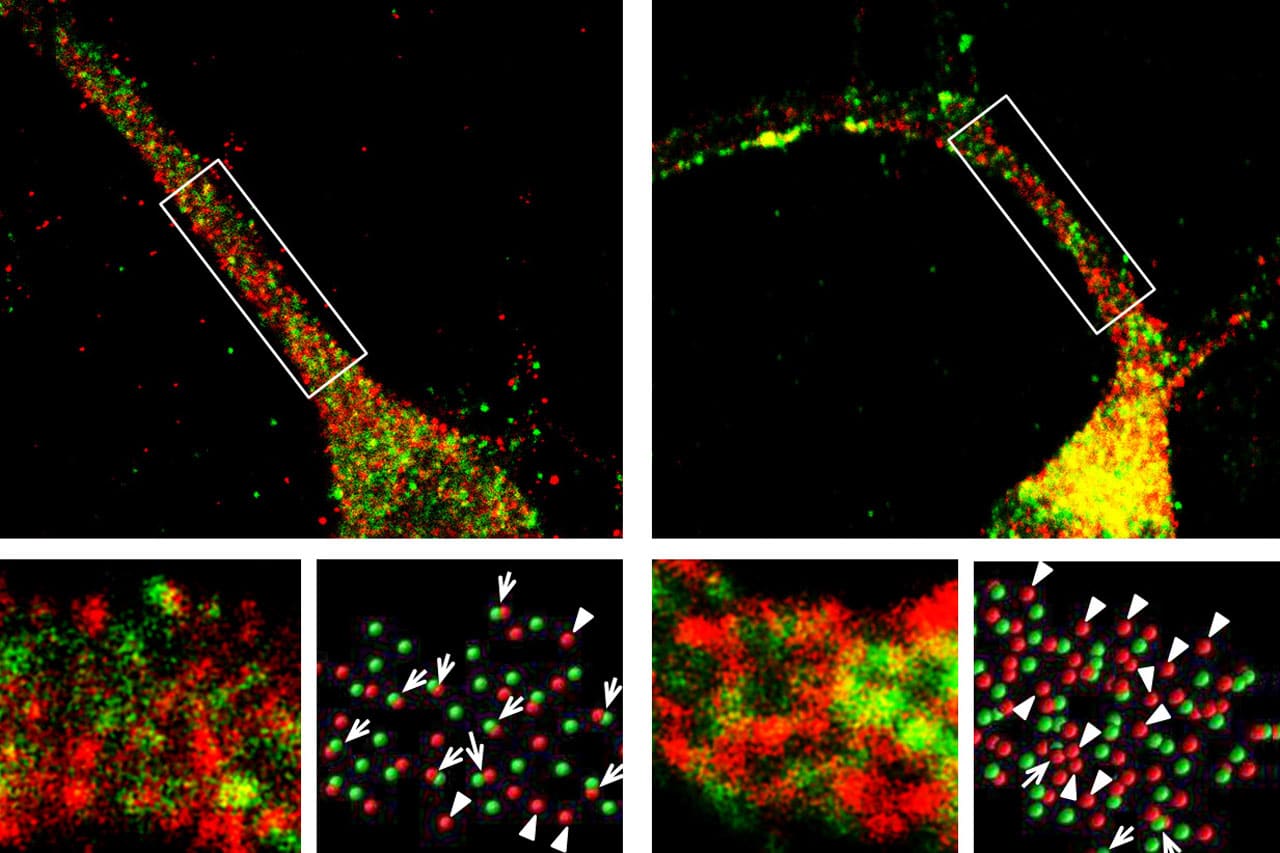
Human speech and language are among the most complex motor and cognitive abilities. The discovery of a mutation in the transcription factor FOXP2 in KE family members with speech disturbances has been a landmark example of the genetic control of vocal communication in humans. Cellular mechanisms underlying this control have remained unclear. A new study […]
Continue reading Scientists learn how changes in a language gene result in speech problems on Tech Explorist.
0 comments:
Post a Comment